Ever wondered just how much data your brain can hold? We often compare the brain to a supercomputer, but what if that comparison isn’t just a metaphor—it’s literal? Deep within your brain, at the junctions where neurons meet, lies an extraordinary form of biological storage: the synapse. And thanks to breakthroughs in information theory, we’re beginning to quantify its staggering capacity.
In this article, we’ll dive into how synaptic storage works, how scientists measure it, and why this knowledge could shape the future of data storage—from artificial intelligence to DNA-based memory.
What Are Synapses and Why Are They Important?
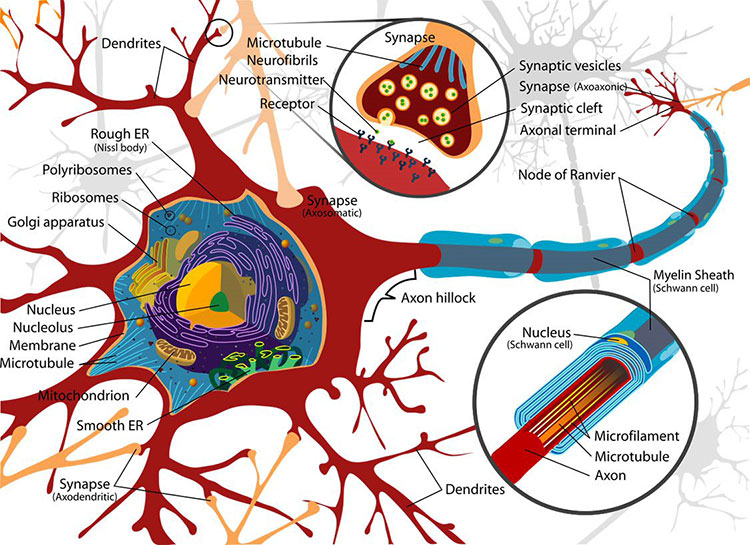
Think of neurons as the brain’s messengers. But without synapses—the gaps between them where signals are transmitted—those messages would go nowhere. A synapse is where the magic happens: it’s the space where one neuron sends a chemical or electrical signal to another, sparking thoughts, memories, movements, and more.
Now here’s the kicker: each of these tiny junctions doesn’t just pass along data—it stores it.
Your brain has about 86 billion neurons, and each one can form around 1,000 synapses. That’s a total of roughly 125 trillion synapses buzzing away in your brain, constantly sending and receiving signals. These connections form the foundation of your memories, knowledge, and perception.
Measuring Synaptic Storage with Information Theory
To understand how synapses store information, scientists turn to information theory—a branch of mathematics that deals with encoding, decoding, and compressing data. Think of it like analyzing how much a hard drive can hold, but on a biological scale.
Video : 2-Minute Neuroscience: Synaptic Transmission
Each synapse, as it turns out, can store up to 4.7 bits of information. That might not sound like much until you consider the scale:
- 1 bit is a single piece of binary data (a 0 or 1)
- 4.7 bits per synapse × 125 trillion synapses = over 500 trillion bits of potential storage
Translated into digital terms, your brain can theoretically store more data than the entire internet—all in a compact, low-energy package powered by biology.
The Brain’s Efficiency: Powering Trillions of Connections
Here’s something even more mind-blowing: while your laptop heats up and guzzles electricity, your brain handles all of this complex storage and processing using roughly 20 watts of power—that’s about the same as a dim light bulb.
This insane efficiency is what’s inspiring researchers to build neural networks and deep learning systems that mimic the brain. If computers could process and store data like synapses do, we’d have faster, smarter, and greener technology.
Artificial Intelligence and Synaptic Models
The field of AI, especially machine learning and deep learning, borrows heavily from how the brain processes and stores information. Artificial neural networks use layers of interconnected nodes (inspired by neurons) to simulate learning.
But here’s where it gets interesting: researchers are now using real data about synaptic information capacity to refine these systems. The goal? To build AI models that are more human-like, not just in intelligence but in efficiency and adaptability.
Imagine a future where your smartphone thinks and stores information with the same elegance as your brain. That future isn’t science fiction—it’s science.
Beyond the Brain: DNA as the Ultimate Storage Device
While the brain remains the pinnacle of biological storage, it’s not the only game in town. Enter DNA, nature’s original information vault.
DNA doesn’t just code for life—it can be used to store digital data. And we’re not talking small files here. A single gram of DNA can hold up to 215 petabytes of data. That’s 215 million gigabytes—enough to store every photo, song, and document you’ve ever owned, plus millions more.
In fact, researchers have already done it. In one groundbreaking study, scientists encoded a 52,000-word book into synthetic DNA. They converted the digital content into binary (0s and 1s), then translated those digits into DNA’s four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, and C. The result? A physical strand of DNA holding a complete, retrievable digital file.
Why DNA Storage Matters for the Future
Traditional storage devices—hard drives, SSDs, even cloud servers—have physical limits. They degrade over time and take up massive amounts of space. DNA, on the other hand, is incredibly compact, durable, and stable for thousands of years if stored properly.
If scaled correctly, DNA storage could revolutionize how we preserve knowledge. Imagine backing up the entire contents of the Library of Congress on something no bigger than a sugar cube. That’s the level we’re talking about.
Video : How Your Brain Remembers: Neurons & Synapses Explained!
Bridging Biology and Technology
What’s exciting is how these two areas—brain synapses and DNA storage—are starting to intersect. Both are nature’s proof that small-scale systems can handle mind-blowing amounts of data. As scientists continue to decode these systems using information theory, they’re finding ways to integrate them into technology.
It’s not about replacing computers with brains or turning DNA into a USB drive. It’s about learning from nature’s most efficient designs to build the next generation of computing and storage systems.
Conclusion: Reimagining Storage in a Biological World
Your brain’s 125 trillion synapses silently store and process more information than entire server farms, all while sipping on 20 watts of energy. Meanwhile, DNA—the code of life—is showing us how to pack massive libraries of data into microscopic strands.
By measuring synaptic storage capacity with information theory, we’re not just understanding the brain better—we’re laying the foundation for a new era of intelligent, efficient technology.
The takeaway? Nature has already solved problems we’re only beginning to understand. And the more we study it, the closer we get to unlocking the true potential of both our minds and our machines.
I Got Married at 80 and My Granddaughter Kicked Me Out – Watch How I Turned the Tables!
When my granddaughter kicked me out after I got married at 80, I knew I had to do something about it. With my new husband, Harold, we came up with a bold plan to show her she couldn’t treat me like that. What followed was a confrontation that changed our family forever.
I never thought I’d be sharing this story, but here we are. My name is Margaret, and I turned 80 last spring. I lived in a cozy room in my granddaughter Ashley’s house. It was small, but I had made it my own, with pictures and keepsakes from my past.

“Good morning, Grandma,” Ashley said one bright Saturday, bursting into my room without knocking. She never bothered with that.
“Morning, dear,” I replied, folding my quilt. “What’s the rush?”
“We’re heading to the park with the kids. Need anything?”
“No, I’m fine. Go enjoy yourself.”
She left quickly, leaving me alone with my thoughts. I couldn’t complain too much — after all, I had sold my house to pay for her college. Her parents had died in a car crash when she was just 15.

I took Ashley in and did my best to give her a good life. Now she lived here with her husband, Brian, and their two kids. Their home was big, lively, and often noisy.
A few months ago, life took an unexpected turn at the community center. I met Harold, who was charming and always had a camera around his neck. We started chatting, and before I knew it, I looked forward to seeing him. It felt like a second chance at love.

One afternoon, while Ashley was at work, I decided to share my news. I found her in the kitchen later that evening, flipping through a recipe book.
“Ashley, I have something to tell you,” I said.
She looked up, “What’s up, Grandma?”
“I’ve met someone. His name is Harold, and… well, he proposed.”
Ashley stared at me, her eyebrows raising in surprise. “Proposed? You mean marriage?”
“Yes,” I replied, trying to contain my smile. “Isn’t it wonderful?”

Her reaction wasn’t what I expected. “Grandma, you’re 80. You’re too old for a wedding dress and all that. And Harold can’t move in here.”
I was shocked. “Why not? We have plenty of space.”
“This is our home. We need our privacy,” she replied firmly.
I tried to reason with her, but she wouldn’t listen. The next morning, she packed my belongings and set them by the door.
“Ashley, what are you doing?” I asked, feeling tears start to form.
“You need to go, Grandma. Find somewhere else to live. Maybe Harold can take you in.”

I couldn’t believe it. After everything I had done for her — raising her, selling my house — she was kicking me out. I felt so betrayed as I looked at the boxes of my life packed up like unwanted clutter.
With few options left, I called Harold. When I told him what happened, he was furious.
“She did what?” he exclaimed. “Margaret, get your things together. I’m coming to get you right now. You’re coming to stay with me.”
I hesitated. “I don’t want to be a burden.”
“You’re not a burden,” he reassured me. “You’re my future wife, and we’re in this together.”

With no other choice, I packed up my belongings and Harold helped me load them into his car. As we drove away, I glanced back at Ashley’s house, feeling a deep sense of sadness.
Harold’s place was a new start. He welcomed me warmly, and I began to feel at home again. We spent our time dreaming about our future together, but the pain from Ashley’s betrayal was hard to shake.
One evening, as we were talking, Harold’s eyes hardened with determination. “We’ll teach her a lesson,” he said firmly. “She needs to understand respect.”

I wasn’t sure how we would make it happen, but I had faith in Harold. He always had a knack for turning ideas into reality.
“Alright,” I said, feeling a surge of confidence. “Let’s show her what we’re capable of.”
And so, we started to plan.
***
Harold and I spent many evenings working on our strategy. Since Harold was a well-known photographer, he came up with a plan to reach Ashley through something she loved. She was passionate about photography and never missed the annual local photographer’s gathering.

“Margaret,” Harold said one evening, “I’ve got a ticket for the gathering. I’ll send it to Ashley anonymously. She won’t be able to resist.”
I felt a thrill of excitement. “Let’s do it.”
Before the big event, Harold and I had a small, intimate wedding.
Harold was determined to capture the day, taking beautiful photographs of our special moments. The photos reflected the joy and love we shared, showing the happiness in my eyes and the warmth between us.

The day of the photography event arrived, and, just as we hoped, Ashley showed up. She had no idea that we were behind the anonymous invitation. Harold and I waited backstage, our nerves tingling with anticipation. We were set on making a statement.
When the host called Harold to the stage to present his award-winning photographs, the room filled with excitement. As Harold walked out, there was a buzz of admiration. Then, to everyone’s surprise, the big screen lit up with portraits of me in my wedding dress.

Gasps filled the room as the audience took in the stunning images of me in my wedding dress. The photos captured not just the beauty of the moment but also the deep emotions we felt.
Harold took the stage and began, “I found love at 79, proving that age is just a number. Margaret, my beautiful wife, has a youthful spirit and a heart full of love.”
I watched as Ashley, sitting in the front row, turned red with embarrassment. Harold handed me the microphone, and I took a deep breath, my heart racing.

“Good evening,” I began, my voice steady. “I want to share a story about sacrifice and love. When my granddaughter Ashley’s parents passed away, I sold my house to help pay for her education and took her in, raising her as my own. But recently, she seemed to forget what love and respect truly mean.”
The room was silent, everyone focused on me. I turned to Ashley, who was sitting in the front row. “Ashley,” I said, “I still love you despite the pain you’ve caused. But I needed you to understand the importance of respect.”
Tears welled up in Ashley’s eyes as she looked down, clearly overwhelmed by the weight of her actions.

Harold spoke up once more, “Margaret and I shared our story to remind everyone that love and respect transcend age. Family should always be about support and understanding.”
The audience erupted into applause, showing their admiration for our message. After the event, Ashley walked up to us, tears streaming down her face.
“Grandma, Harold,” she said, her voice trembling, “I am so sorry. I was wrong and disrespectful. Can you ever forgive me?”
Harold and I exchanged a look, then I wrapped Ashley in a warm hug. “Of course, dear. We love you. We just needed you to understand.”

She invited us to a family dinner, promising to support my happiness and never take me for granted again. We accepted, hopeful for a fresh start.
That evening, we joined Ashley and her family. The atmosphere was warm, with sincere efforts to mend our relationship. Laughter and conversation flowed easily, and for the first time in a long while, I felt truly at peace.
During dinner, Ashley looked at me with sincere eyes. “Grandma, I didn’t realize how much I hurt you. I was selfish and ungrateful.”

“It’s okay, Ashley,” I said, gently placing my hand on hers. “What matters is that we move forward together.”
Brian, Ashley’s husband, who had been quiet throughout, finally spoke up: “We’re happy you’re content, Margaret. And Harold, you seem like a great guy. We’re lucky to have you both in our lives.”
Harold smiled warmly. “Thank you, Brian. We’re glad to be here.”
The children, sensing the shift in the mood, eagerly showed us their latest drawings and school projects. It was heartwarming to see the family reconnect. The room was filled with a genuine sense of togetherness, and I felt a renewed sense of belonging.

As the evening went on, Harold shared more about our adventures and how we met. Ashley listened closely, her eyes occasionally moist with tears. It was clear she felt truly sorry and wanted to make things right.
After dinner, we settled in the living room with cups of tea. Ashley turned to me again, her voice earnest. “Grandma, I want you to move back in with us. We have plenty of room, and I promise things will be different.”
I glanced at Harold, who nodded in agreement. “We appreciate the offer, Ashley, but Harold and I have our own home now. We’ll visit often, though.”

Ashley gave a bittersweet smile, showing she understood. “I get it. I just want you to be happy.”
“I am happy,” I told her. “And so are you. That’s what matters.”
As we left that night, the moonlight softly illuminating our path, I thought about the importance of self-love and standing up for oneself. Sometimes, life’s greatest joys come when we least expect them.
Looking around the table, I felt a deep gratitude for the second chance at happiness and for the family that, despite everything, remained close to my heart.

Harold and I drove home in quiet reflection, each of us processing the day’s events. When we arrived, he took my hand gently and said, “We did it, Margaret. We really did.”
I smiled, feeling a mix of accomplishment and relief. “Yes, we did. And this is just the beginning.”
Harold kissed my hand, and together, we walked into our home, ready for whatever came next. Our love and determination had delivered a powerful lesson to Ashley, and it had brought us all closer. This was a new chapter, brimming with hope and endless possibilities.

That sounds like a story with a lot of emotional depth and growth! If you enjoyed the previous tale, this one about a grandson’s change of heart and his quest for forgiveness should be quite compelling. Here’s a glimpse of what might unfold in that story:
**Title:** “Grandson Called Grandma ‘The Worst’ for Not Giving Gifts—Years Later, He Begged for Forgiveness”
**Summary:**
Once, a young grandson harshly labeled his grandmother “the worst” because she couldn’t afford to buy him presents. Her heart was broken, but she understood that his youthful perspective didn’t grasp the full picture. Over the years, as he grew older and faced his own challenges, he came to realize the depth of his mistake. Now, he seeks forgiveness and hopes to mend the rift caused by his earlier selfishness.
**Key Themes:**
– **Understanding and Growth:** The journey from being a self-centered child to a more empathetic adult.
– **Family and Forgiveness:** The importance of reconciling and valuing loved ones.
– **Life Lessons:** Learning the true meaning of generosity and love beyond material gifts.
If this piques your interest, diving into the full story could offer a touching look at personal redemption and the strength of familial bonds.



Leave a Reply