The Captivating Beauty and Hidden Danger of Cross Seas
Nature never ceases to amaze with its ability to produce breathtaking phenomena, offering us moments of awe and wonder. Among these marvels is the striking display of cross seas—a rare and visually stunning oceanic pattern where waves intersect to create intricate, grid-like formations.
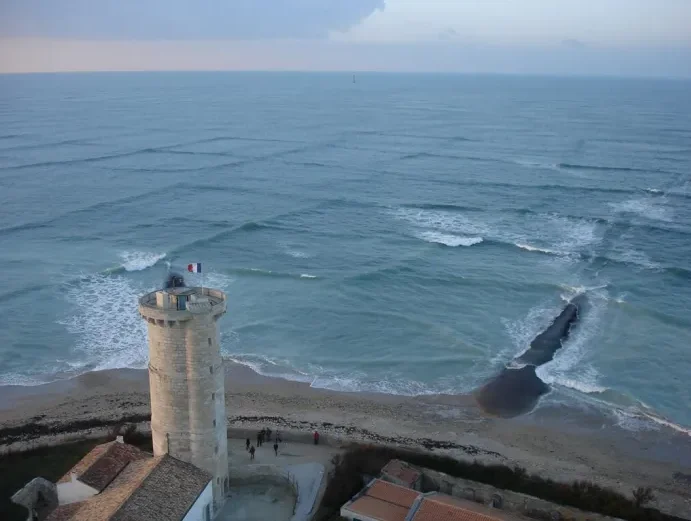

Cross seas occur when two wave systems converge at angles greater than 45 degrees, or when wind-driven waves clash with a swell traveling in a different direction. While these watery grids are undeniably beautiful, they are also deceptively dangerous, posing serious risks to both swimmers and vessels.
Beneath their enchanting surface lies a hazardous reality. The currents generated by cross seas can be unpredictable and powerful, making them perilous for those in the water. Navigating a boat or ship through these conditions is especially challenging, often leading to accidents and shipwrecks. Experts attribute many maritime incidents to the dangers of cross seas.
A 2010 report by the European Space Agency highlighted how frequently these conditions occur, particularly when wind-driven waves and swells overlap. According to a 2004 study cited by the agency, a significant proportion of ship accidents were linked to crossing sea states, underscoring the need for caution in these waters.
One location where this phenomenon is particularly visible is along the western coast of France, especially near Île de Ré. Tourists flock to witness the mesmerizing patterns, though entering the water is strongly discouraged due to the extreme risks. Instead, visitors can safely admire the view from a lighthouse on the island’s western side.
Cross seas serve as a reminder of nature’s duality—its ability to inspire wonder while demanding respect for its inherent dangers. For a closer look at this extraordinary phenomenon, check out the video below. Nature’s beauty continues to captivate us, blending awe with caution.
This Will Happen to Your Body If You Eat Ginger Every Day for One Month
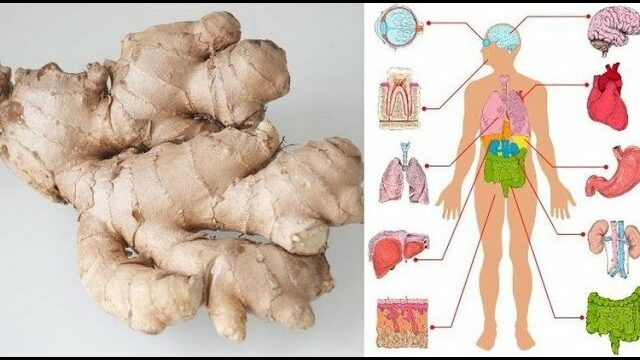
Ginger has been used for centuries as a natural remedy—and for good reason. If you add a small amount of ginger to your daily routine, the changes you’ll notice in just one month might surprise you. From digestion to immunity, this spicy root supports your health in gentle but powerful ways.
1. Better Digestion
Ginger is known to stimulate digestive enzymes, reduce bloating, and ease discomfort after meals. Eating a bit of ginger daily can help your stomach feel lighter and more comfortable.
2. Reduced Inflammation and Joint Pain
Thanks to its natural anti-inflammatory compounds like gingerol, daily ginger can help ease stiffness and discomfort in joints and muscles. Many people notice less swelling and more mobility within a few weeks.
3. Improved Circulation
Ginger naturally warms the body and helps stimulate blood flow, which supports heart health and keeps your extremities from feeling cold or stiff.
4. Stronger Immunity
Ginger has antibacterial and antiviral properties that help protect against colds and infections. With daily use, your immune system may become more resilient—especially during seasonal changes.
5. Balanced Blood Sugar and Cholesterol
Studies suggest that ginger may help regulate blood sugar levels and improve cholesterol balance, making it a smart choice for long-term health support.
6. Clearer Skin and Fewer Breakouts
Its detoxifying effects and anti-inflammatory action can also support cleaner, brighter skin over time, especially when combined with a healthy diet.
How to Use Ginger Daily
- Grate fresh ginger into hot water for a calming tea
- Add it to soups, smoothies, or stir-fries
- Chew a small raw slice in the morning (if you like the spice)
A little goes a long way—just 1–2 grams of fresh ginger daily is enough to feel the benefits.
One Month, Many Benefits
With just a small daily habit, ginger can support your body from head to toe. After one month, you might feel lighter, more energized, and more in tune with your health—naturally and deliciously.



Leave a Reply