Ever wondered just how much data your brain can hold? We often compare the brain to a supercomputer, but what if that comparison isn’t just a metaphor—it’s literal? Deep within your brain, at the junctions where neurons meet, lies an extraordinary form of biological storage: the synapse. And thanks to breakthroughs in information theory, we’re beginning to quantify its staggering capacity.
In this article, we’ll dive into how synaptic storage works, how scientists measure it, and why this knowledge could shape the future of data storage—from artificial intelligence to DNA-based memory.
What Are Synapses and Why Are They Important?
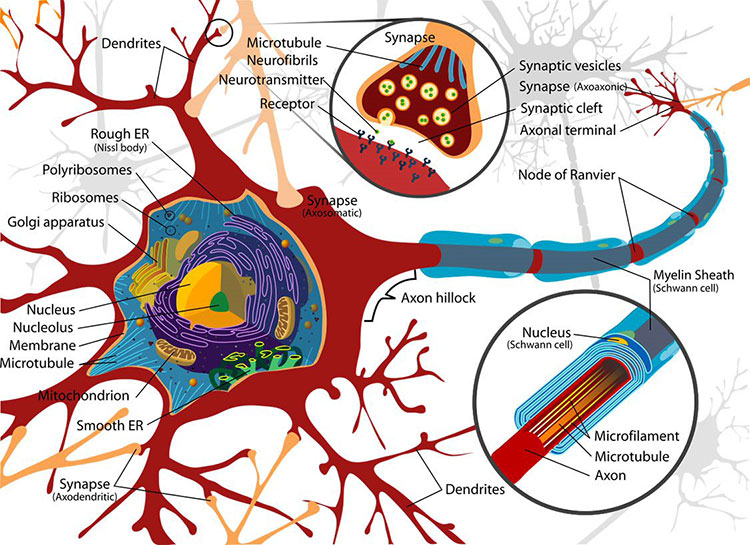
Think of neurons as the brain’s messengers. But without synapses—the gaps between them where signals are transmitted—those messages would go nowhere. A synapse is where the magic happens: it’s the space where one neuron sends a chemical or electrical signal to another, sparking thoughts, memories, movements, and more.
Now here’s the kicker: each of these tiny junctions doesn’t just pass along data—it stores it.
Your brain has about 86 billion neurons, and each one can form around 1,000 synapses. That’s a total of roughly 125 trillion synapses buzzing away in your brain, constantly sending and receiving signals. These connections form the foundation of your memories, knowledge, and perception.
Measuring Synaptic Storage with Information Theory
To understand how synapses store information, scientists turn to information theory—a branch of mathematics that deals with encoding, decoding, and compressing data. Think of it like analyzing how much a hard drive can hold, but on a biological scale.
Video : 2-Minute Neuroscience: Synaptic Transmission
Each synapse, as it turns out, can store up to 4.7 bits of information. That might not sound like much until you consider the scale:
- 1 bit is a single piece of binary data (a 0 or 1)
- 4.7 bits per synapse × 125 trillion synapses = over 500 trillion bits of potential storage
Translated into digital terms, your brain can theoretically store more data than the entire internet—all in a compact, low-energy package powered by biology.
The Brain’s Efficiency: Powering Trillions of Connections
Here’s something even more mind-blowing: while your laptop heats up and guzzles electricity, your brain handles all of this complex storage and processing using roughly 20 watts of power—that’s about the same as a dim light bulb.
This insane efficiency is what’s inspiring researchers to build neural networks and deep learning systems that mimic the brain. If computers could process and store data like synapses do, we’d have faster, smarter, and greener technology.
Artificial Intelligence and Synaptic Models
The field of AI, especially machine learning and deep learning, borrows heavily from how the brain processes and stores information. Artificial neural networks use layers of interconnected nodes (inspired by neurons) to simulate learning.
But here’s where it gets interesting: researchers are now using real data about synaptic information capacity to refine these systems. The goal? To build AI models that are more human-like, not just in intelligence but in efficiency and adaptability.
Imagine a future where your smartphone thinks and stores information with the same elegance as your brain. That future isn’t science fiction—it’s science.
Beyond the Brain: DNA as the Ultimate Storage Device
While the brain remains the pinnacle of biological storage, it’s not the only game in town. Enter DNA, nature’s original information vault.
DNA doesn’t just code for life—it can be used to store digital data. And we’re not talking small files here. A single gram of DNA can hold up to 215 petabytes of data. That’s 215 million gigabytes—enough to store every photo, song, and document you’ve ever owned, plus millions more.
In fact, researchers have already done it. In one groundbreaking study, scientists encoded a 52,000-word book into synthetic DNA. They converted the digital content into binary (0s and 1s), then translated those digits into DNA’s four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, and C. The result? A physical strand of DNA holding a complete, retrievable digital file.
Why DNA Storage Matters for the Future
Traditional storage devices—hard drives, SSDs, even cloud servers—have physical limits. They degrade over time and take up massive amounts of space. DNA, on the other hand, is incredibly compact, durable, and stable for thousands of years if stored properly.
If scaled correctly, DNA storage could revolutionize how we preserve knowledge. Imagine backing up the entire contents of the Library of Congress on something no bigger than a sugar cube. That’s the level we’re talking about.
Video : How Your Brain Remembers: Neurons & Synapses Explained!
Bridging Biology and Technology
What’s exciting is how these two areas—brain synapses and DNA storage—are starting to intersect. Both are nature’s proof that small-scale systems can handle mind-blowing amounts of data. As scientists continue to decode these systems using information theory, they’re finding ways to integrate them into technology.
It’s not about replacing computers with brains or turning DNA into a USB drive. It’s about learning from nature’s most efficient designs to build the next generation of computing and storage systems.
Conclusion: Reimagining Storage in a Biological World
Your brain’s 125 trillion synapses silently store and process more information than entire server farms, all while sipping on 20 watts of energy. Meanwhile, DNA—the code of life—is showing us how to pack massive libraries of data into microscopic strands.
By measuring synaptic storage capacity with information theory, we’re not just understanding the brain better—we’re laying the foundation for a new era of intelligent, efficient technology.
The takeaway? Nature has already solved problems we’re only beginning to understand. And the more we study it, the closer we get to unlocking the true potential of both our minds and our machines.
While I was on vacation, my wealthy neighbor constructed a fence on my property, obstructing my windows — I delivered a flawless lesson in return

After a week of sun and sand, Catherine was shocked to discover her new neighbor Jeffrey had built an imposing fence on her property. As a single mom, she couldn’t let this slide. What did she do to teach him a lesson he’d never forget?
Life as a single mom isn’t easy, but I’ve been making it work. I’m Catherine, 40 years old, and I’ve been raising my two boys, Liam (10) and Chris (8), all by myself for the past year.
Their father and I parted ways when I caught him cheating with another woman. Well, that’s a story for another time.
About two months ago, I bought a new house and moved in with my kids. It’s in a peaceful neighborhood with a beautiful forest nearby.
Everything about our new neighborhood seemed perfect until I met my next-door neighbor, Jeffrey. We had been at odds since the beginning.
I’ll never forget our first interaction.
It had been a day since we moved in when I heard a knock at my door. I opened it and saw him standing at my doorstep with a folder in his hand.
“Hello there, neighbor!” he said, extending his hand. “I’m Jeffrey. Welcome to the neighborhood!”
I shook his hand.
How nice! I thought. If only I knew what was coming in the days ahead.
“I wanted to discuss something important with you,” he continued, opening his folder.
“The previous owners signed this contract allowing me to build a fence on the property line.”
I raised an eyebrow. “Okay…?”
“So, I’ll be starting construction next week,” he said matter-of-factly.
I was stunned. “Excuse me? You’re not even asking for my permission?”
“Well, I have the contract right here—”
“That contract was with the previous owners,” I interrupted. “I’m the owner now, and I don’t want a fence blocking my view and sunlight.”
That’s when his face turned red.
“But I need this fence for privacy!” he yelled. “I’ve been planning this for months!”
“Why should I care about what the FORMER owner said?” I asked, but I never got a straight answer.
I just saw Jeffrey stomp out of my house.
Since that day, he’s been arguing with me almost every week about this fence. Apparently, he wants to host fancy garden parties without his guests seeing into my yard.
Well, excuse me for existing!
I couldn’t let him build that fence. I didn’t buy this house to stare at wooden planks instead of the beautiful sky and trees.
Little did I know, things were about to get much worse.
A few weeks ago, I decided to take my boys on a much-needed vacation. Liam and Chris were bouncing off the walls with excitement.
“Mom, can we go to the beach?” Liam asked.
Chris chimed in, “Yeah! And can we build a huge sandcastle?”
“Of course, boys!” I said as I hugged them. “We’ll do all that and more!”
We left for a week, looking forward to sun, sand, and relaxation. If only I’d known what was waiting for us when we got back.
As we pulled into our driveway, I noticed something odd. My heart sank as I realized what had happened.
“Boys, stay in the car for a minute,” I said as I got out.
My blood boiled with each step I took toward our house.
As I peeked to the right, I realized what had happened. There, right in front of our windows, stood a tall wooden fence. On our property. One foot from my windows!
“What the hell?!” I shouted, not caring who heard me.
Liam and Chris came running up behind me.
“Mom, what’s wrong?” Chris asked in a worried voice.
I took a deep breath. I had to stay calm for their sake. “Nothing, sweetie. Just a little… surprise from our neighbor.”
“But Mom,” Liam said, frowning, “we can’t see the trees anymore.”
My heart broke.
Jeffrey’s stupid fence had replaced the beautiful view from our windows that my boys loved so much. Now, we couldn’t even see the sky!
I couldn’t let this slide. I had to teach Jeffrey a lesson.
I had two options. Either take the legal route and wait for the authorities to take action or take matters into my own hands.
I chose the second one because my boys and I didn’t have enough time to take the legal route.
Later that night, I went to the pet store. I had a plan that I knew would work.
“Can I help you find anything?” the clerk asked.
I smiled sweetly. “Yes, I’m looking for an animal attractant spray. The strongest you have.”
After returning home, I waited until the neighborhood was asleep. Then, I went up to his precious fence and poured an entire bottle of the attractant liquid.
The pheromone scent was strong. It was designed to attract dogs for training purposes. But I had a feeling it might attract more than just dogs.
I did this for several nights in a row, ensuring the solution covered every inch of the fence.
Then, I waited.
It didn’t take long for results to show.
One night, as I was taking out the trash, I saw a stray dog lift its leg against the fence. I had to stifle a laugh.
“Good boy,” I whispered.
Over the next few days, more and more animals started visiting the fence. Foxes, raccoons, even a moose once! They all seemed to think Jeffrey’s fence was the perfect place to do their business.
I watched from my window as Jeffrey discovered the mess one morning. His face turned an impressive shade of purple as he realized what was happening.
But to my surprise, he didn’t take down the fence.
He started cleaning it.
Every morning, Jeffrey would come out with a bucket and scrub brush, muttering under his breath as he cleaned off the nightly deposits.
But no matter how much he cleaned, he couldn’t get rid of the pheromone scent. The animals kept coming back, night after night.
Soon, the smell became unbearable. Even my boys started to notice.
“Mom,” Chris said one day, holding his nose, “it stinks outside!”
Liam nodded in agreement. “Yeah, can we play inside today?”
“I know it smells bad, boys,” I said. “Just give it a few more days, okay?”
They nodded, but I could see they were disappointed. I hoped my plan would work soon.
The next day, I was coming back from a grocery run when I saw one of our other neighbors, Mrs. Thompson, knocking on Jeffrey’s door.
I slowed down, pretending to check my mail as I eavesdropped.
“Jeffrey,” Mrs. Thompson began, “what on earth is that smell coming from your yard? It’s awful!”
Jeffrey seemed so embarrassed.
“I… I’m working on it, Mrs. Thompson. There’s been a bit of an animal problem.”
“Well, work faster!” she snapped. “It’s affecting the whole neighborhood!”
As Mrs. Thompson stormed off, Jeffrey caught my eye. He had this apologetic look on his face that I had never seen before. I smiled at him and quickly walked into my house.
That evening, I watched from my other window as Jeffrey attacked the fence with every cleaning product known to man.
He scrubbed and sprayed for hours, but the smell lingered. Finally, he threw down his brush in defeat and trudged back to his house.
The next morning, I was awakened by a loud noise outside. I peeked through my curtains and had to blink a few times to make sure I wasn’t dreaming.
I could see Jeffrey overseeing a team of workers as they took down the fence.
I couldn’t believe my plan had actually worked!
I woke up the boys with the good news. “Liam! Chris! Come look outside!”
They raced to the window, their eyes widening as they saw the fence coming down.
“Mom, we can see the trees again!” Chris exclaimed.
Liam hugged me tight. “You’re the best, Mom!”
And with that, our view was restored, and Jeffrey had learned his lesson. However, the story doesn’t end there.
Later that day, Jeffrey approached me while I was gardening in the front yard.
“Catherine,” he started, clearing his throat, “I, uh… I want to apologize.”
“Oh?” I pretended to act surprised.
He nodded. “I shouldn’t have put up that fence without your permission. It was wrong of me.”
“Yes, it was,” I agreed, crossing my arms.
“I’ve learned my lesson,” he continued. “From now on, I’ll respect your property and your rights as a neighbor.”
“Apology accepted, Jeffrey,” I smiled. “Let’s start over, shall we?”
“I’d like that.”
As Jeffrey walked away, I couldn’t help but feel proud. I had stood up for myself and my boys, and in the end, everything worked out.
That incident taught me that life sometimes puts you in situations where you have to get creative to find a solution, just like I had to come up with a plan to teach Jeffrey a lesson he’ll never forget.
Do you think I did the right thing?



Leave a Reply